HDU (2045 不容易系列之(3)—— LELE的RPG难题)
题目大意:有排成一行的n个方格,用红(Red)、粉(Pink)、绿(Green)三色涂每个格子,每格涂一色,要求任何相邻的方格不能同色,且首尾两格也不同色.求全部的满足要求的涂法.
题目分析:
这个题目刚刚开始,规律是找出来了,但是边界木有考虑好啊!
首先来分析一下:
假设求N个格子有多少种图法:
1)当N-1个与第一个相同颜色,所以这种图法不合法,从而映射出,第N-2个肯定合法!所以这时候我们有两种图法,即不用考虑第N-1个,只用考虑N-2合法的染法种类数 : 2*F[ N-2];
2) 当N-1个与第一个不相同,说明从第一个到第N-1个都是合法的图法,我们就不用考虑太多,这里只能用一种颜色了,您想啊,头用了一种颜色,N-1用了一种颜色,第N个既不能与第一个相同,又不能与第N-1个相同,那么只有一种颜色了,这时候只用考虑N-1的长度的合法种类: F[ n-1]
F[ N ] = F[ N-1 ]+2* F [ N-2 ];
但是这里要考虑边界问题!
f[1]=3;
f[2]=6;
f[3]=6;
这里的三个格子比较特殊,因为总公才3种颜色,相邻,头尾颜色各异,所以个数为2的 与格子数为3的 图法一样
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
double s[55]={0};
int main(){
int i,n;
s[1]=3;
s[2]=6;
s[3]=6;
for(i=4;i<=50;i++)
s[i]=s[i-2]*2+s[i-1];
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){
printf("%.0lf\n",s[n]);
}
return 0;
}
HDU 1055(Number Sequence) 典型的找循环节的题目!
题目:
f(1) = 1, f(2) = 1, f(n) = (A * f(n - 1) + B * f(n - 2)) mod 7.
Given A, B, and n, you are to calculate the value of f(n).
For each test case, print the value of f(n) on a single line.
题目分析:
这种题目第一次做,学会了 什么时候找循环节!因为这种题目,数据量那么大 ,肯定有循环节的!
这里我就是以找到与第1个跟第2个等的两个数作为一个循环节!因为每个数都是由前面两个数决定的!所以循环节要找到第一对 与第1个与第2个匹配的!
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int f[1009];
int main(){
int a,b,n,i,c;
f[1]=f[2]=1;
while(scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&n),a || b || n){
for(i=3;i<50;i++){
f[i]=(a*f[i-1]+b*f[i-2])%7;
if(f[i]==1&&f[i-1]==1)
break;
}
c=i-2;
n=n%c;
if(n==0)
printf("%d\n",f[c]);
else
printf("%d\n",f[n]);
}
return 0;
}
HDU 1290 2050 (切蛋糕 折线分平面--二维,三维 的分割区间问题)
题目:
|
Problem Description
或许你曾经牢骚满腹
或许你依然心怀忧伤 或许你近在咫尺 或许你我天各一方 对于每一个学子 母校 永远航行在 生命的海洋 今年是我们杭电建校五十周年,这是一个值得祝福的日子。我们该送给母校一个怎样的礼物呢?对于目前的大家来说,最好的礼物当然是省赛中的好成绩,我不能参赛,就送给学校一个DOOM III球形大蛋糕吧,这可是名牌,估计要花掉我半年的银子呢。 想象着正式校庆那一天,校长亲自操刀,把这个大蛋糕分给各地赶来祝贺的校友们,大家一定很高兴,呵呵,流口水了吧... 等一等,吃蛋糕之前先考大家一个问题:如果校长大人在蛋糕上切了N刀(校长刀法极好,每一刀都是一个绝对的平面),最多可以把这个球形蛋糕切成几块呢? 做不出这个题目,没有蛋糕吃的! 为-了-母-校-,为-了-蛋-糕-(不是为了DGMM,枫之羽最会浮想联翩...),加-油-! |
|
Input
输入数据包含多个测试实例,每个实例占一行,每行包含一个整数n(1<=n<=1000),表示切的刀数。
|
|
Output
对于每组输入数据,请输出对应的蛋糕块数,每个测试实例输出一行。
|
|
Sample Input
1 2 3 |
|
Sample Output
2 4 8 |
这种题目有公式可以套的s[n] = (n^3 + 5n)/6 +1
文章最后会给出这一类问题的 模板公式,只需具体问题,待定系数去解就可以了 ,很方便
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)){
int ans=(n*n*n+5*n)/6+1;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
2050题目:
折线分割平面Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5605 Accepted Submission(s): 4007
Problem Description
我们看到过很多直线分割平面的题目,今天的这个题目稍微有些变化,我们要求的是n条折线分割平面的最大数目。比如,一条折线可以将平面分成两部分,两条折线最多可以将平面分成7部分,具体如下所示。
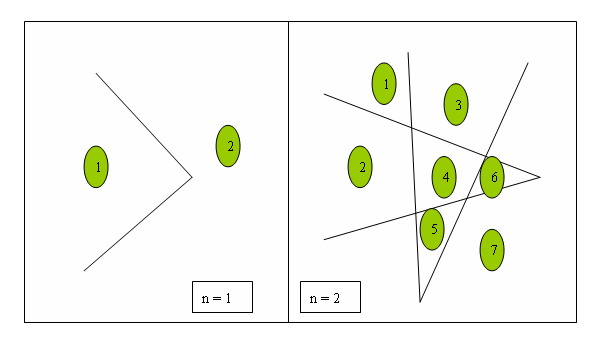
Input
输入数据的第一行是一个整数C,表示测试实例的个数,然后是C 行数据,每行包含一个整数n(0<n<=10000),表示折线的数量。
Output
对于每个测试实例,请输出平面的最大分割数,每个实例的输出占一行。
Sample Input
2 1 2
Sample Output
2 7 |
这个题目的公式:s[n] = 2*n^2 - n +1;
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int cas,n;
scanf("%d",&cas);
while(cas--){
scanf("%d",&n);
int ans=2*n*n-n+1;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
总结:
其实这类题目都有模板公式的,只许具体问题,您带入几个解去求出各个系数就可以了!
一般二维的是 a*n^2 +b *n +c
三维的是: a*n^3 + b* n^2 + c*n +d
具体问题带定系数法求出各个系数就OK了,不用想破脑筋找规律。。。。。。
HDU 1222(Wolf and Rabbit)约瑟夫最小公倍数问题
|
Problem Description
There is a hill with n holes around. The holes are signed from 0 to n-1.
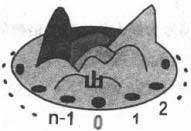 A rabbit must hide in one of the holes. A wolf searches the rabbit in anticlockwise order. The first hole he get into is the one signed with 0. Then he will get into the hole every m holes. For example, m=2 and n=6, the wolf will get into the holes which are signed 0,2,4,0. If the rabbit hides in the hole which signed 1,3 or 5, she will survive. So we call these holes the safe holes. |
|
Input
The input starts with a positive integer P which indicates the number of test cases. Then on the following P lines,each line consists 2 positive integer m and n(0<m,n<2147483648).
|
|
Output
For each input m n, if safe holes exist, you should output "YES", else output "NO" in a single line. |
|
Sample Input
2 1 2 2 2 |
|
Sample Output
NO YES |
题目分析:
假设步长是m 总长度是N, 这里首先我们计算出他们的周期,也就是最小公倍数,当过了这个周期,狼搜索的点肯定重复了!
因为狼每走一次肯定是搜索了一个点,搜索完n个点的时候,走的长度正好是这个周期,说明他没有重复的搜索了N个点!你可以在纸上画一下
其实不难理解!
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int x,int y){
int c;
if(x<y){
c=x; x=y;
y=c;
}
if(y==0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y,x%y);
}
int main(){
int cas,n,m;
scanf("%d",&cas);
while(cas--){
scanf("%d %d",&m,&n);
printf(gcd(n,m)==1?"NO\n":"YES\n");
}
return 0;
}
HDU 1997(汉诺塔VII 思想很NB)
题目大意;
|
Problem Description
n个盘子的汉诺塔问题的最少移动次数是2^n-1,即在移动过程中会产生2^n个系列。由于发生错移产生的系列就增加了,这种错误是放错了柱子,并不会把大盘放到小盘上,即各柱子从下往上的大小仍保持如下关系 :
n=m+p+q a1>a2>...>am b1>b2>...>bp c1>c2>...>cq ai是A柱上的盘的盘号系列,bi是B柱上的盘的盘号系列, ci是C柱上的盘的盘号系列,最初目标是将A柱上的n个盘子移到C盘. 给出1个系列,判断它是否是在正确的移动中产生的系列. 例1:n=3 3 2 1 是正确的 例2:n=3 3 1 2 是不正确的。 注:对于例2如果目标是将A柱上的n个盘子移到B盘. 则是正确的. |
|
Input
包含多组数据,首先输入T,表示有T组数据.每组数据4行,第1行N是盘子的数目N<=64.
后3行如下 m a1 a2 ...am p b1 b2 ...bp q c1 c2 ...cq N=m+p+q,0<=m<=N,0<=p<=N,0<=q<=N, |
|
Output
对于每组数据,判断它是否是在正确的移动中产生的系列.正确输出true,否则false |
|
Sample Input
6 3 1 3 1 2 1 1 3 1 3 1 1 1 2 6 3 6 5 4 1 1 2 3 2 6 3 6 5 4 2 3 2 1 1 3 1 3 1 2 1 1 20 2 20 17 2 19 18 16 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 |
|
Sample Output
true false false false true true 这个题目幸好只是判断他是不是最优化的,不然真的TBT了,我也是刚刚才能理解,网上解题报告几乎都没说什么思路,琢磨了好久~ 其实 1) 最初我们要判断一下是不是已经完全放好了,这样就不用考虑是不是最优化了, 因为都已经放好了,肯定是最合法的! 或者说全部在A上,这是还没开始动作的一个状态,所以也是合法的! 2) 否则我们 要对每次状态的最大的那个进行判断,因为我们知道,汉诺塔最大的那个不可能停在B上,(假设 最初的时候都在A上,要移到C上去!),只可能在A或者C上面!如果是放在B上面,停止判断,直接断定他非法~这样我们得出了第二个判段依据! 3)如果最大的在A上面,我可以想到的是,他还没有放在C上,此时这个状态的上面一系列状态都是想把其他的放在B上,然后就可以把A放到C上了,所以我们在这里做出更新,因为他上面一系列动作都是想让A上面的除最大的外都放到B上面去,所以,我们这个时候往上考虑,对N-1进行 判断!这个时候动作的方向是A->B所以为了统一操作,我们得把B跟C互换! 4)如果最大的在C上面,这时候倒数第二大的不是放在B上就是C上,我们要把要把倒数第二大的以及其他的放在C上,这时候的动作方向是B—>C;所以把A跟B交换一下! 代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int one[4],n[4],h[4][1000];
int a,b,c,i,N;
int cas,t;
bool flag;
scanf("%d",&cas);
while(cas--){
a=1; b=2; c=3;
one[a]=1,one[b]=1,one[c]=1;
scanf("%d",&N);
scanf("%d",&n[a]);
for(i=one[a];i<=n[a];i++)
scanf("%d",&h[a][i]);
scanf("%d",&n[b]);
for(i=one[b];i<=n[b];i++)
scanf("%d",&h[b][i]);
scanf("%d",&n[c]);
for(i=one[c];i<=n[c];i++)
scanf("%d",&h[c][i]);
while(1){
if(n[c]==N||n[a]==N){
flag=true;
break;
}
if(n[b]>0&&h[b][one[b]]==N){
flag=false;
break;
}
if(n[a]>0&&h[a][one[a]]==N){
N--;
n[a]--;
one[a]++;
t=b; b=c;
c=t;
continue;
}
if(h[c][one[c]]==N&&n[c]>0){
N--;
n[c]--;
one[c]++;
t=b; b=a;
a=t;
continue;
}
}
if(flag)
printf("true\n");
else
printf("false\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
HDU 1443( Joseph 约瑟夫问题 )
Suppose that there are k good guys and k bad guys. In the circle the first k are good guys and the last k bad guys. You have to determine such minimal m that all the bad guys will be executed before the first good guy.
3 4 0
5 30
题目分析:这个题目我目前没找到更好的办法,上网没查到,唉,我的代码跑了500MS 郁闷死了!我是用枚举+模拟的
思路:
for i : 1 -> 14
for j : i ->
然后分别用长度位2 * i, 周期为 j 的循环模拟,
solve( k ,m ) :
每次都是用 kill = (m - 1)%i (这是求本次需要去除的元素的下标)
更新: start=((start-m)%i+i)%i ( 其实也可以写成 :start =( (start - kill -1) %i + i )%i )
end=((end - m ) % i + i ) % i; 同理也可以写成上面的那样!
示例:
1(0) 2(1) 3(2) 4(3) 5(4) 6(5)
假设 :周期为5
第一次: kill = ( 5-1)%6=4(因为数组里下标4 就是第5个元素)
然后关键地方 start=(( 0 - 5 )%6+6) %6=1 这里就是关键: 此时 1(1) 2(2) 3(3) 4(4) 6(0)
同理 end=((2-5)%6+6)%6 =3;
这个时候 我们把数组 的顺序做个变动 按下标 重新 排列!
6(0) 1(1) 2(2) 3(3) 4(4)
这样不是又重复了上述过程麽? 但是start 与end 的指向 永远都是
没变 还是指向那几个元素!
就这样整个模拟过程的准备工作都完成了!
源程序+部分注释:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int f[15];
bool solve(int k,int m){
bool flag=true;
int start=0,end=k-1,kill;
for(int i=2*k;i>k;i--){
kill=(m-1)%i;
//cout<<"i = "<<i<<" "<<"kill = "<<kill<<endl;
if(kill>=start&&kill<=end){
flag=false;
break;
}
start=((start-m)%i+i)%i;
end=((end-m)%i+i)%i;//这样是为了更新起始点,以当前点为0坐标!想象成一个圆形!
//cout<<"start = "<<start<<" "<<" end = "<<end<<endl;
}
return flag;
}
int main(){
int n;
for(int i=1;i<=14;i++){
for(int j=i;;j++){
if(solve(i,j)){
f[i]=j;
break;
}
}
}
while(~scanf("%d",&n),n){
printf("%d\n",f[n]);
}
return 0;
}
题目总结: 注意学习,模拟约瑟夫循环的过程!
三个方程:
kill = ( m - 1 ) % n
start = ( (start - m) % n +n )%n
end = ((end - m )%n +n)% n;
上述的n是当前的长度,是动态的!